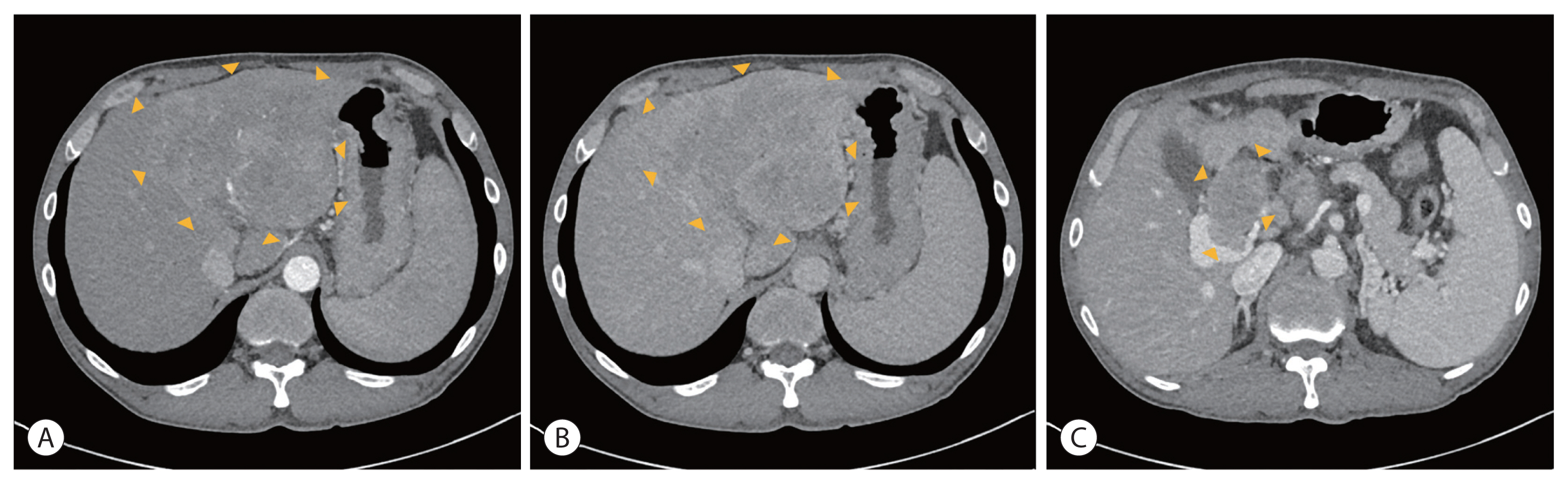
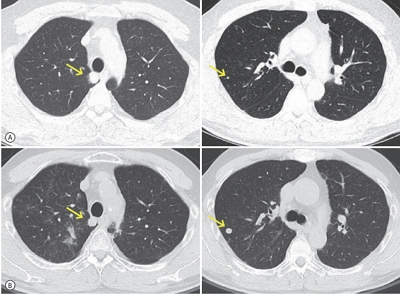
- Multidisciplinary treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma
-
Ahlim Lee, Jaejun Lee, Hyun Yang, Soo-Yoon Sung, Chang Ho Jeon, Su Ho Kim, Moon Hyung Choi, Young Joon Lee, Ho Jong Chun, Si Hyun Bae
-
J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):75-83. Published online March 18, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.04
-
-
3,972
Views
-
93
Downloads
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a cytotoxic chemotherapy-resistant tumor and most HCCs arise in a background of liver cirrhosis of various causes. Although the IMBrave150 trial showed remarkable advancements in the treatment of unresectable HCC with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva), therapeutic outcomes were unsatisfactory in more than half of the patients. Accordingly, many ongoing trials combine conventional modalities with new drugs such as immune checkpoint inhibitors for better treatment outcomes, and they are expected to benefit patients with limited responses to conventional treatment. Here, two patients with advanced stage HCC with preserved liver function and good performance status showed partial response after treatment with combination or sequential therapy of AteBeva, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and transarterial chemoembolization. These findings indicate the efficacy of multidisciplinary treatment against advanced HCC. Additional studies are required to establish optimal treatment strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Diagnostic performance of serum exosomal miRNA-720 in hepatocellular carcinoma
-
Jeong Won Jang, Ji Min Kim, Hye Seon Kim, Jin Seoub Kim, Ji Won Han, Soon Kyu Lee, Heechul Nam, Pil Soo Sung, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):30-39. Published online March 21, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.02.25
-
-
3,850
Views
-
131
Downloads
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
- Background/Aim
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with poor prognosis, largely due to late detection. Highly accurate biomarkers are urgently needed to detect early-stage HCC. Our study aims to explore the diagnostic performance of serum exosomal microRNA (miR)-720 in HCC.
Methods
Exosomal miRNA was measured via quantitative real-time PCR. A correlation analysis of exosomal miR-720 and tumor or clinico-demographic data of patients with HCC was performed. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to assess the diagnostic capacity of serum exosomal miR-720 for HCC, in comparison with α-fetoprotein (AFP) and prothrombin induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II).
Results
MiR-720 was chosen as a potential HCC marker via miR microarray based on significant differential expression between tumor and non-tumor samples. Serum exosomal miR-720 was significantly upregulated in patients with HCC (n=114) versus other liver diseases (control, n=30), with a higher area under the ROC curve (AUC=0.931) than the other markers. Particularly, serum exosomal miR-720 showed superior performance in diagnosing small HCC (< 5 cm; AUC=0.930) compared with AFP (AUC=0.802) or PIVKA-II (AUC=0.718). Exosomal miR-720 levels showed marginal correlation with tumor size. The proportion of elevated miR-720 also increased with intrahepatic tumor stage progression. Unlike AFP or PIVKA-II showing a significant correlation with aminotransferase levels, the exosomal miR-720 level was not affected by aminotransferase levels.
Conclusions
Serum exosomal miR-720 is an excellent biomarker for the diagnosis of HCC, with better performance than AFP or PIVKA-II. Its diagnostic utility is maintained even in small HCC and is unaffected by aminotransferase levels.
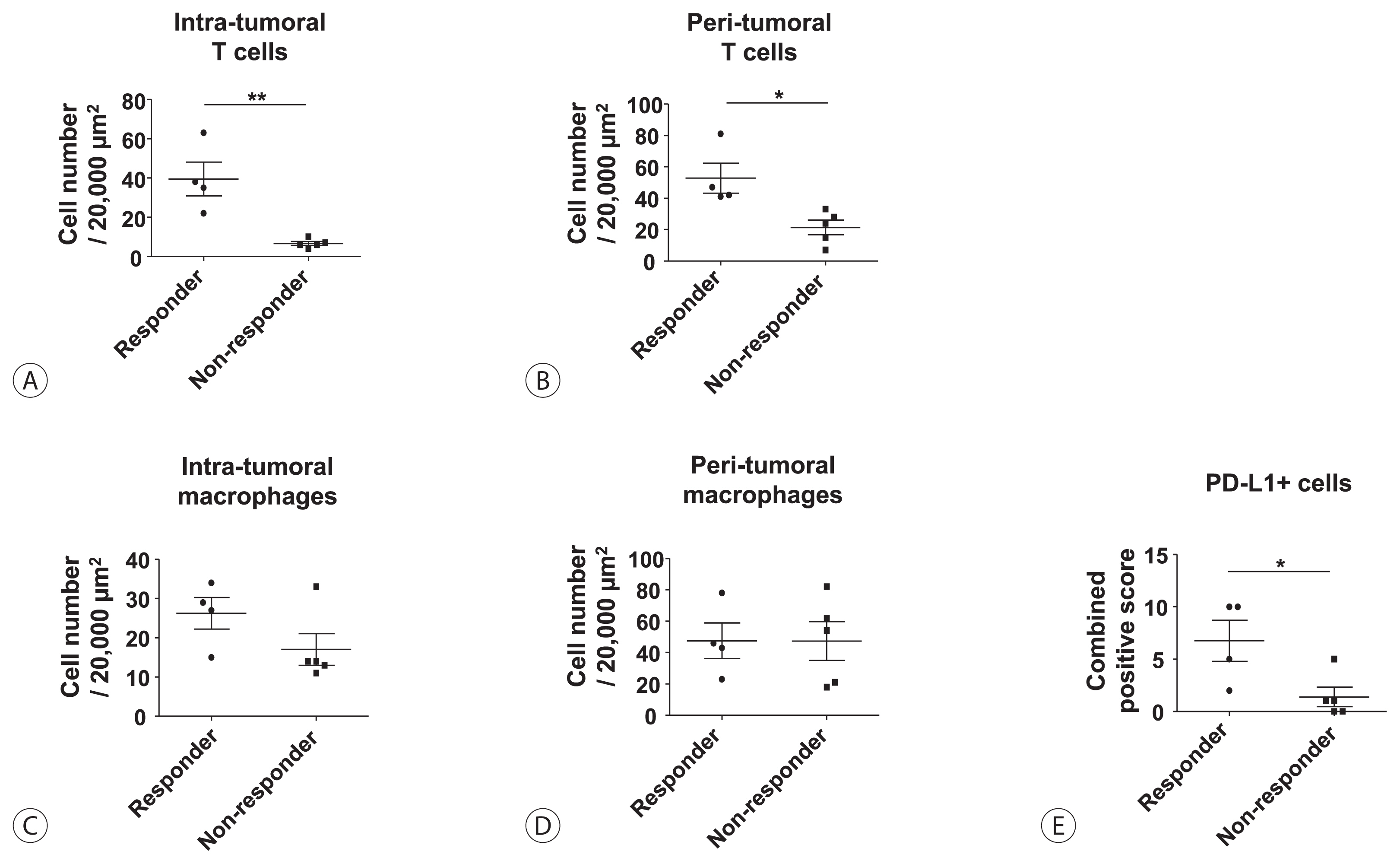
- Infiltration of T Cells and Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1-expressing Macrophages as a Potential Predictor of Lenvatinib Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Pil Soo Sung, Sung Woo Cho, Jaejun Lee, Hyun Yang, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):128-134. Published online September 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.128
-
-
3,275
Views
-
98
Downloads
-
6
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background/Aim
s: Lenvatinib was recently proven to be non-inferior to sorafenib in treating unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in a phase-3 randomized controlled trial. In this study, we investigated whether the response to lenvatinib was affected by tumor immunogenicity.
Methods
Between May 2019 and April 2020, nine patients with intermediate-to-advanced HCC, who were treated with lenvatinib after liver biopsy, were enrolled. Immunohistochemical staining and multi-color flow cytometry were performed on specimens obtained from liver biopsy.
Results
Among the nine patients enrolled, four showed objective responses (complete responses+partial responses). Immunohistochemical staining for CD3, CD68, and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) demonstrated that patients with objective responses showed marked infiltration of T cells and PD-L1-expressing macrophages in intra-tumoral and peri-tumoral tissues compared to those without objective responses. A significant difference in the numbers of infiltrated T cells, both in the intra-tumoral (P<0.01) and peri-tumoral regions (P<0.05), were identified between responders and non-responders. Regarding the number of infiltrated macrophages, no significant difference was found between the responders and non-responders, although the number of PD-L1-expressing tumor-associated macrophages was significantly higher in responders than that in non-responders (P<0.05).
Conclusions
Tumor immunogenicity, as indicated by T cell and PD-L1-positive macrophage infiltration, affects lenvatinib response in unresectable HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Higher Number of Tumor-Infiltrating PD-L1+ Cells Is Related to Better Response to Multikinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Won Han, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Hyun Kim, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Hyun Yang, Pil Soo Sung
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1453. CrossRef - Intrahepatic inflammatory IgA+PD-L1high monocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma development and immunotherapy
Pil Soo Sung, Dong Jun Park, Pu Reun Roh, Kyoung Do Mun, Sung Woo Cho, Gil Won Lee, Eun Sun Jung, Sung Hak Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Jonghwan Choi, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2022; 10(5): e003618. CrossRef - Crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and neighboring cells in hepatocellular carcinoma
Pil Soo Sung
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(3): 333. CrossRef - Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go
Pil Soo Sung, Isaac Kise Lee, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunological Mechanisms for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk after Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Pil Soo Sung, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(2): 221. CrossRef - Preferential Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Protein in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Its Potential Role in Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Dong-Jun Park, Pil-Soo Sung, Gil-Won Lee, Sung-Woo Cho, Sung-Min Kim, Byung-Yoon Kang, Won-Hee Hur, Hyun Yang, Soon-Kyu Lee, Sung-Hak Lee, Eun-Sun Jung, Chang-Ho Seo, Joseph Ahn, Ho-Joong Choi, Young-Kyoung You, Jeong-Won Jang, Si-Hyun Bae, Jong-Young Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4710. CrossRef
- Successful Sequential Therapy Involving Regorafenib after Failure of Sorafenib in a Patient with Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation
-
Soon Kyu Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Heechul Nam, Pil Soo Sung, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):84-89. Published online March 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.84
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The efficacy and safety of sequential systemic therapy for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after liver transplantation (LT) are not well established. This study describes a successful experience where sequential therapy with sorafenib followed by regorafenib was used to treat recurrent HCC in a 54-year old male LT recipient. After HCC recurred in both lungs 10 months after LT, sorafenib was administered with radiation therapy to treat pulmonary metastases. However, after 4 months of sorafenib treatment showed progressive pulmonary metastases, sequential regorafenib treatment was started. After 3 months (cycles) of regorafenib treatment, tumor response was partial, and after 6 months (cycles), disease status remained stable without signs of progression or drug-related serious adverse events. This case suggests that sequential systemic therapy is feasible in patient with recurrent HCC after LT.
- Early Onset Polymorphic Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease Mimicking a Solitary Necrotizing Abscess in a Graft Liver
-
Pil Soo Sung, Jaejun Lee, Joon Lee, Hee Chul Nam, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):165-170. Published online September 30, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.165
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Although post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) after liver transplantation is very rare, its prognosis is worse than that of PTLD following other types of solid organ transplantation. Here, we report a rare case of early onset polymorphic PTLD in a graft liver occurring five months after deceased-donor liver transplantation due to hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C virus infection. Initially, findings from contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging mistakenly suspected the lesion was a necrotizing abscess with central necrosis. However, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and biopsy findings confirmed an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated, B cell type polymorphic PTLD with central necrosis. Our case suggests regular monitoring of EBV serologic status for liver transplant recipients who were initially in an EBV seronegative state. Although early-onset PTLD is very rare after liver transplantation, PTLD should be suspected when recipients show the seroconversion for EBV proteins and the development of new tumors with various clinical presentations.
- High-level Expression of Interleukin-17 and C-reactive Protein Predicts Tumor Progression in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated by Transarterial Chemoembolization
-
Myeong Jun Song, Sung Won Lee, Eun-Jee Oh, Bohyun Jang, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):108-117. Published online September 30, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.108
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background/Aim
s: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the standard locoregional
treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Angiogenesis and
inflammation play important roles in tumor growth in HCC. In this study, we evaluated the
associations between the levels of growth factors and inflammatory markers and clinical
prognosis in patients with unresectable HCC treated with TACE.
Methods
The clinical outcomes of 58 HCC patients treated with TACE at the Catholic Medical
Centers from January, 2012 to February 2015 were evaluated. Baseline levels of the growth
factors vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth
factor, and hepatocyte growth factor and the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and
high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were compared with the treatment outcomes. The
primary endpoint was time to progression (TTP); the secondary endpoint was overall survival
(OS).
Results
During the 20.8 months of follow-up, TTP was significantly delayed in patients with
low levels of hs-CRP (≤0.15) and IL-17 (≤0.94) and a maximal tumor diameter ≤5 cm (P =0.010,
P =0.015, and 0.048, respectively). Patients with HCC with low hs-CRP and IL-17 levels had
a longer survival than that of those with high hs-CRP levels and IL-17 (35.1 vs. 22.5 months,
P =0.000; 41 vs. 21.8 months, P =0.000, respectively). However, any baseline growth factors
were not significantly correlated with TTP and OS.
Conclusions
Elevated IL-17 and hs-CRP may be predictive of a poor outcome in patients
with HCC treated with TACE. A better understanding of this relationship will require further
investigation of the immune mechanisms underlying tumor progression.
- A Case of Complete Response by Multidisciplinary Management in a Patient with Solitary Bone Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Seawon Hwang, Hyun Yang, Hae Lim Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):52-56. Published online March 31, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.52
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Despite recent advances in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the prognosis
of patients with extrahepatic metastasis from HCC still remains dismal. The current study
presents a case of HCC that was metastatic to the pelvis and describes successful treatment
with multidisciplinary approach to the skeletal metastasis. The patient was a 67-year-old
male who presented with right pelvic pain 28 months following right hepatectomy for HCC.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging indicated a solitary bone metastasis
without intrahepatic recurrence. Complete response was achieved with multidisciplinary
management including sorafenib, transarterial embolization, surgery to remove the
metastatic mass and radiotherapy after surgery. A post-operative follow-up 15 months later
found that the patient remained in good health with maintained complete response. This case
suggests that a multidisciplinary approach can achieve long-term cancer-free survival and
prolonged life expectancy beyond palliative care for patients with solitary bone metastasis
after curative surgery for HCC.
- Comparative Study between Metronomic Chemotherapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Child-Pugh Class B Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Hyun Yang, Myeong Jun Song, Hee Chul Nam, Hae Lim Lee, Sung Won Lee, Do Seon Song, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Yong Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
-
J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(2):92-99. Published online September 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.2.92
-
-
1,302
Views
-
7
Downloads
-
1
Citation
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background/Aim
s: Metronomic (MET) chemotherapy is a treatment characterized by
frequent infusion of low doses of chemotherapeutic agent without extended break. The aim
of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of MET chemotherapy compared with transarterial
chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with child B class advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC).
Methods
Seventy-three patients with child B class advanced HCC were analyzed between
April, 2007 and August, 2013 according to two treatment groups: (i) MET chemotherapy group
(n=43, Epirubicin 35 mg/body surface area [BSA] every 4 weeks, and cisplatin 15 mg/BSA and
5-fluorouracil 50 mg/BSA weekly for 3 weeks) via an implantable port system with 1 week
break. (ii) TACE group (n=30, Adriamycin 20-50 mg) every 4 weeks. Primary endpoint was
overall survival (OS).
Results
The median survival times in the MET and TACE groups were 4.5 months and
3.1 months, respectively. The overall survival rate showed significantly better in the MET
treatment group than in the TACE group (P=0.039). When the factors affecting patient
OS were analyzed, MET chemotherapy (P=0.038, hazard ratio {HR} 0.538 [95% confidence
interval {CI} 0.299-0.967]) was independently associated with OS. Larger maximal tumor size,
extrahepatic metastasis and advanced stage also were significant factors for OS (P=0.009, HR
1.064 [95% CI 1.014-16.064]; P=0.014, HR 2.120 [95% CI 1.164-3.861]; P=0.019, HR 2.046 [95% CI
1.125-3.720], respectively).
Conclusions
MET chemotherapy showed survival benefit than TACE in patients with child
class B advanced HCC. Therefore, MET chemotherapy may be considered as a treatment
option for advanced HCC with poor liver function. (J Liver Cancer 2015;15:92-99)
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparative study of sorafenib and metronomic chemotherapy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer-stage C hepatocellular carcinoma with poor liver function
Hyun Yang, Hyun Young Woo, Soon Kyu Lee, Ji Won Han, Bohyun Jang, Hee Chul Nam, Hae Lim Lee, Sung Won Lee, Do Seon Song, Myeong Jun Song, Jung Suk Oh, Ho Jong Chun, Jeong Won Jang, Angelo Lozada, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2017; 23(2): 128. CrossRef
- A Case of Combination Therapy Using Radioembolization and Transarterial Chemoembolization with Drug-eluting Beads in Bilobar Hepatocellular Carcinomas
-
Hee Yeon Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Do Seon Song, Myeong Jun Song, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Si Hyun Bae, Ho Jung Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):128-132. Published online September 30, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Bilobar multifocal hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) can be treated with transarterial radioembolization in a sequential lobar, or whole liver manner. However, radioembolization could result in a risk of radiation-induced liver toxicity in patients with reduced functional reserve. Here we describe a case with bilobar HCCs successfully treated with a combination therapy using radioembolization and transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads without significant side effects. A 72-year-old female with liver cirrhosis was diagnosed of hepatocellular carcinoma with bilobar involvement. The main mass in the left lobe was treated with radioembolization while the other lesion in the right lobe was treated with transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads, and the patient was tolerable. A combination of radioembolization and selective transarterial chemoem- bolization may be considered for an alternative option in patients with bilobar multifocal HCCs with decreased liver function.
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma which Showed Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization with DC Bead® in the Patient who Showed No Response to Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization
-
Do Seon Song, Hee Yeon Kim, Myeong Jun Song, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Ho Jong Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):133-136. Published online September 30, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most important cause of cancer death in South Korea. Approximately two thirds
of the HCC patients are diagnosed in the unresectable stage. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) showed
survival benefit in the unresectable HCC patients, but it had some limitations, such as low response rate and systemic toxicity.
Drug eluting bead has been reported low systemic toxicity and higher tumor necrosis rate. We report a case which showed
response to TACE with DC bead in patient that showed no response to conventional TACE.
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a 10 Year Old Child Treated with Yttrium Radioembolization and Transarterial Chemoembolization
-
Sung Won Lee, Hee Yeon Kim, Do Seon Song, Chung-Hwa Park, Myeong Jun Song, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Jung Suk Oh, Ho Jong Chun, Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):137-140. Published online September 30, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in childhood is rare but is the second most common malignant liver neoplasm after
hepatoblastoma in children. Surgical resectability is the foundation of curative therapy but only one third of newly diagnosed
HCCs are resectable, and unresectable HCC remains largely unresponsive to systemic chemotherapy. In all reported series of
HCC in children, therapeutic results are poor with overall survival less than 30%. Systemic chemotherapy is only partially
effective but if preoperative downstaging can be achieved, it would result in a higher survival rate. There are scarce data
regarding local ablative treatments such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and therefore survival benefits are still
unclear. TACE may be considered as a therapeutic alternative in cases of unresectable tumors after systemic chemotherapy or in
unresectable, non-metastatic HCCs. The use of orthotopic liver transplantation in childhood HCC remains controversial.
Radioembolization is a mode of treatment that aims to selectively target radiation to all liver tumors using yttrium-90
microspheres while limiting the dose to normal liver parenchyma. It may be considered as another treatment option in childhood
HCC with the purpose of preoperative downstaging but further studies are required to determine the treatment benefits and safety
of radioembolization treatment.
- A Case of Progressive Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis after Percutaneous Transhepatic Obliteration in Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinomaswith Portal Vein Thrombosis
-
Hee Yeon Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Sung won Lee, Do Seon Song, Myeong Jun Song, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Si Hyun Bae, Jung Suk Oh, Ho Jong Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):146-150. Published online September 30, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Percutaneous transhepatic obliteration of gastroesophageal varices is one of the effective emergency procedure when
endoscopic therapy is not indicated or has been failed. One of the major complications of this procedure is portal thrombosis. A
53-year-old male with hepatitis B virus infection was diagnosed of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with right portal vein
thrombosis. On the next day after being hospitalization, the patient developed variceal bleeding. With medical management,
endoscopic therapy was initially attempted, however, it ended in failure. Emergency percutaneous transhepatic obliteration of
bleeding gastroesophageal varices was considered as a next option. Bleeding from gastroesophageal varices was stopped after
percutaneous obliateration, however, portal thrombosis was extended to splenic vein or superior mesenteric veins.
- Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Myeong Jun Song, Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):5-9. Published online February 28, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Surgery, percutaneous ablation and liver
transplantation are the only curative treatment modality for HCC. However, a majority of patients have unresectable disease at
diagnosis. Despite radical treatment, high risk of tumor recurrence is the most common problem. Therefore, there is a need for
effective treatment options for patients with advanced or recurrent HCC. For patients with advanced stage of HCC according to
the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system, the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib is the current standard of care. However,
hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) have been applied to advanced stage HCC with a view to improve the therapeutic
indexes in Asia. HAIC provides direct drug delivery into tumor bed and a greater first‐pass effect; also systemic side effects can
be potentially minimized. However, the sample size of researches on HAIC was small and large randomized trials are still
lacking. In this article, we describe the treatment efficacy of HAIC for advanced stage HCC and discuss future therapeutic
possibilities.
- A Case of Liver Transplantation after Combination of Sorafenib and Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in the Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient with Portal Vein Thrombosis
-
Do Seon Song, Myeong Jun Song, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Ho Jong Chun, Dong Goo Kim
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):62-66. Published online February 28, 2012
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most common malignancy in Korea where chronic hepatitis B virus is prevalent.
More than 60-70% of HCC cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage that are not eligible for curative therapy such as surgical
resection, liver transplantation, radiofrequency ablation, and percutaneous ethanol injection. According to Barcellona Clinic
Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging and treatment, standard treatment of advanced HCC is sorafenib. And there are some reports that
hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) could be a beneficial therapeutic option for patients with advanced HCC. We
report a case of advanced HCC with portal vein thrombosis that received liver transplantation after combination treatment of
HAIC and sorafenib.
- Changes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Guidelines during the Last Ten-Year Period
-
Do Seon Song, Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):136-143. Published online September 30, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most common cause of cancer death in the world. There has been many advances
in diagnosis of HCC during the last ten-year period, especially imaging techniques. The Korean Liver cancer study group
(KLCSG), European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), American Association for the Study of Liver disease
(AASLD) and Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of Liver (APASL) have made and changed HCC guidelines with advances
of imaging technique and results of research on HCC. We reviewed the changes of imaging guidelines in HCC diagnosis
according to the advances of imaging. In addition, further studies will be needed to solve the controversies in diagnosis of HCC
smaller than 1 cm in size.
- Complications Associated with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Sun Hong Yoo, Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):144-148. Published online September 30, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is one of the most effective treatments for patients with inoperable
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, variable complications can occur after TACE. Complications resulting from TACE
contain postembolization syndrome, liver abscess, bile duct injury, ruptured HCC, acute hepatic failure, variceal bleeding, acute
kidney injury, pulmonary lipiodol embolization, femoral artery pseudoaneurysm, femoral arteriovenous fistula, abdominal aortic
dissection, spinal cord injury, and others. Complications after TACE are occasionally fatal. Therefore, it is important that we are
well acquainted ourselves with these complications, and need care promptly the patient who develop symptoms of complication.
- Conus Medullaris Syndrome after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Sun Hong Yoo, Si Hyun Bae, Pil Soo Sung, Hee Yeon Kim, Do Seon Song, Myeong Jun Song, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Ho Jong Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):185-189. Published online September 30, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth most common cancer in Korea and a common cause of cancer death.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is used as palliative therapy for patients with inoperable HCC. TACE is an
effective treatments for inoperable HCC, but variable complications due to using embolic agents can occur after TACE.
Complications due to embolic agents include pulmonary lipiodol embolism, splenic infarction, cerebral lipiodol infarction, and
spinal cord injury. This is a rare case of spinal cord injury after a sixth TACE via right T9 intercostal artery.
- From Down Staging to Curative Treatment: Based on Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient
-
Chung-Hwa Park, Myung Joon Song, Seung Kew Yoon, Jong Young Choi, Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(1):46-49. Published online February 28, 2011
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) is performed in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in
which locoregional therapeutic methods such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI)
or radiofrequency ablation (RFA) could not be the best choice. Sorafenib, the only approved systemic chemotherapeutic agent
for HCC, improves survival rate, but is associated with a low tumor response rate. Thus combining these therapeutic modalities to
treat HCC in advanced stage may help downstaging and leading to better treatment results without taking risk for hepatic failure.
Here we report a case treated to a complete remission by combining HAIC, PEI and sorafenib.
- A Case of Complete Remission in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Metronomic Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy
-
Myeong Jon Song, CHung-Hwa Park, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Ho Jong Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2010;10(1):35-39. Published online June 30, 2010
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 53-year-old man patient was admitted for evaluation of abdominal pain. Liver dynamic CT showed infiltrative type mass
in right hepatic angle with arterial enhancement and rapid washout. Also low density tumor thrombus is filled with in right
portal vein. He was diagnosed HCC (UICC stage IVa) with liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class B). With the sixth cycle of metronomic
hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy for infiltrative mass, HCC showed no stain in hepatic angiography and tumor marker
are normalized at seven month from initial diagnosis.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed with Metastatic Lesion of the Cervical Spine
-
Chung-Hwa Park, Myeong Jun Song, Hee Yeon Kim, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon, Jong Young Choi
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2010;10(1):61-63. Published online June 30, 2010
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Bone metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are usually treated with non-operative procedures such as radiotherapy,
hormonal therapy, bisphosphonates, or sometimes with surgical procedures. Here we describe a case with 3rd cervical spine
metastasis of HCC. A 62-year-old female with liver cirrhosis presented with neck pain. After evaluation, the patient was
diagnosed of hepatocellular carcinoma with cervical spine metastasis. The metastatic lesion was treated with tomotherapy
while the primary lesion in the liver was treated with transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads, and the
patient is tolerable waiting for the next treatment.
- Is the treatment needed for massive hepatocellular carcinoma? Pros
-
Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):7-12. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Although advanced HCCs larger than 10 cm in diameter are still often seen, the survival benefit and safety of the
treatments for patients with huge hepatocellular carcinoma is uncertain. With conservative management, median survival in
patients whose huge tumor invades the main portal vein is approximately 3 months. Surgical resection is the only way to
cure the disease for patients with big tumours. However, huge tumors frequently present with poor liver reserve, vascular
invasion and intrahepatic dissemination, all the factors limit the resectability of huge HCC. Transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization (TACE) is a main palliative treatment for unresectable HCC. For unresectable HCC larger than 10 cm
in diameter, TACE is the only treatment option. Responses to transarterial chemotherapy are infrequent and there exists
considerable skepticism as to the value of the therapy because it could give rise to excessive liver damage for huge HCCs.
The recent study suggests that patients with HCC larger than 10 cm in diameter are not suitable candidates for TACE
treatment because of a high mortality rate due to serious side effects. Whether TACE is beneficial or not for this type of
patient deserves further study. Several investigators have sought to delineate potential benefits of various therapies, although
the lack of consensus regarding standards of care in advanced HCC. There are only a limited number of reports to date
focusing on TACE for patients with HCC larger than 10 cm in diameter. Herein, we conducted this retrospective, case–
control study to elucidate the outcome of multimodal therapies based on TACE for patients with huge unresectable HCC and
determine the factors that are independently associated with the survival.
- Early Intrahepatic Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Metastasis to Lung and Brain after Radiofrequency Ablation
-
Jin Dong Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Young Jun Lee, Sung Eun Rha, Ho Jong Chun, Byung Gil Choi, Hae Giu Lee
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):37-40. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the preferred method of local ablation for patients with small (<3 cm sized)
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) when surgical resection cannot be applied. If RFA procedure is sufficiently completed, it
provides lower local tumor recurrence, and longer overall as well as disease-free survival. We experienced a case of early
stage HCC which recurred at 2 months after successful RFA procedure, and rapidly metastasized to lung and brain.
- Rapid recurrence following living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria
-
Hyun Young Woo, Jin Dong Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Sung Eun Rha, Jae Young Byun, Ho Jong Chun, Byung Gil Choi, Hae Kyu Lee, Young Kyoung You, Dong Gu Kim
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):45-48. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Liver transplantation is curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma especially if ,within Milan criteria, 4 year survival
and recurrence-free survival was reported to be 85% and 92%, respectively. Herein we report a patient who experience rapid
recurrence following living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) for hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. A 52
year-old-men patient with known liver cirrhosis associated with hepatitis B virus was admitted for the treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Abdominal CT revealed two nodules less than 3 cm in right hepatic lobe. After single
session of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), the patient underwent LDLT. After seven months following
transplantation, recurrent HCC was detected on transplanted liver with concurrent metastatic nodule in lung. Although TACE
and metastsectomy were performed for recurrent intrahepatic mass and lung metastasis, recurrent HCC showed rapid
progression and patient died of progressive tumor after 10 months following LDLT.
- Treatment of Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Invasion
-
Jung Hyun Kwon, Jong Young Choi, Jin Dong Kim, Hyun Young Woo, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon, Young Jun Lee, Ho Jong Chun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):53-58. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 52 year-old-man patient was admitted for evaluation of hepatic mass which was detected on screening ultrasonography.
His abdominal CT showed a massive infiltrating mass in left hepatic lobe and another 2.4 cm nodule in S6 of Rt. Hepatic
lobe with arterial enhancement and rapid wash out underlying liver cirrhosis. Also, low density tumor thrombus are filled
in Lt. portal vein and extended into main portal vein. He was finally diagnosed HCC (UICC stage IVa) with liver cirrhosis
(Child-Pugh class A) and hepatitis B. With the four times of trasnarterial chemo-lipiodolization and seven times of
intraarterial infusion chemotherapy for huge mass and one time Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for daughter nodule, his HCC
showed no stain in hepatic angiogram at nine month from initial diagnosis. After additional eight times of intra-arterial
infusion chemotherapy, new small nodule developed in S6 and was ablated with RFA. At eighteen months after initial
diagnosis, he shows no viable lesion on the imaging study and tumor markers are normalized.
- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Twenties Treated by Multimodality Therapy
-
Jang Eun Lee, Na Ri Yoon, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Dong Goo Kim, Ho Jong Chun, Byung Gil Choi, Hae Giu Lee, Hong Seok Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Eun Sun Jang
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):82-85. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The prognosis of young patients with hepatocellular carcinoma is remains controversial. Here we report a case of advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma in twenty, successfully treated with transarterial chemolipidolization (TACL), systemic chemotherapy,
radiation therapy and surgical resection. Previously healthy 28 years old woman was admitted for treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Abdominal CT showed a diffuse infiltrative HCC involving both lobes with intrahepatic bile duct invasion and
pericardial lymphadenopathy. She was treated TAC with systemic chemotherapy and external beam radiotherapy. 6 months
after these treatments, main tumor and the pericardial lymph node were decreased in size. And then extended left lobectomy
and systemic chemotherapy were done. The pericardial lymph node was markedly decreased. The patient has been followed
for 10 months without evidence of regional tumor recurrence.
- A Case of the Complete Remission of a Solitary Extrahepatic Bile Duct Hepatocellular Carcinoma without Primary Hepatic Parenchymal Lesions by Cyberknife Treatment
-
Soung Won Jeong, Si Hyun Bae, Hyun Young Woo, Chan Ran You, Won Hang Hur, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Dong Hoon Lee, Young Jun Lee, Jae Young Byun, Hong Seok Jang
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):92-97. Published online June 30, 2008
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 69-year-old man patient was hospitalized by confused mentality. He had chronic hepatitis B virus infection
and was diagnosed with liver cirrhosis 20 years ago. Abdominal CT showed about 2×1 cm sized polypoid mass
with mild arterial enhancement at the S4 of liver, causing moderate dilatation of the left IHBD. In the CTHA-AP,
intraductal mass was hyperattenuated at arterial phase and washed out at portal phase. Celiac angiography
revealed nodular tumor staining correlating to intraductal mass on CT. In MRCP and ERCP, a polypoid lesion was
noted at the orifice of left main intrahepatic duct. The patient was treated with cyber-knife for 3 days with 3600
cGy. In follow up CT after 2 month of cyber-knife treatment, there was regression of previously noted left IHBD
dilatation and no definite enhancing intraductal mass.
- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Achieving Complete Response with New Therapeutic Modalities
-
Hyun Young Woo, Jin Dong Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Chan Ran You, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Se Hyun Cho, Seung Kew Yoon, Dong Hoon Lee, Ho Jong Chun, Byung Gil Choi, Chul Seung Kay
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):124-127. Published online June 30, 2008
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 45-year-old man was admitted for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). He was diagnosed
hepatitis B carrier 16 years ago and has not done a routine check. Abdominal CT showed a diffuse infiltrative
HCC involving right hepatic lobe with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) involving right portal vein and
proximal portion of left portal vein umbilical portion. With concurrent transcatheter arterial chemotherapy (TAC),
helical tomotherapy for portal vein thrombosis was done. With these treatments, main tumor and PVTT was
decreased in size markedly and no stain in hepatic angiogram. Due to repeated TAC, hepatic arterial stenosis
occurred and TAC was stopped. 3 months after, recurrent tumor was detected in MRI. Radiofrequency ablation
followed by High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) was done for this recurrent mass. No viable mass was
shown in the follow up MRI done 6 months after HIFU.
- Tumorigenesis of Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
-
Si Hyun Bae
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):8-12. Published online June 30, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (CHC) is an extremely rare form of primary liver cancer having
features of both hepatocellular and biliary epithelial differentiation. The incidence of CHC was 1.0-6.3% of all
primary liver cancers.
Since Allen and LIsa first described the features of this tumor in 1949, Allen’s classification has been widely
used. This classification includes: type A, double cancer of HCC and CC, with HCC and CC present at different
sites without contact; type B, HCC and CC are present at adjacent sites and mingle with continued growth; and
type C, HCC and CC are mixed, growing within the same tumor. CHC are often confused with pseudoglandular
growth pattern in HCC, but this has led to the mistaken impression that CHC are common. Histologically, only
type C displays the characteristic of genuine mixture of both HCC and CC elements, and only Allen’s type C was
included and regarded as true CHC in many published studies of CHC. With regard to the tumorigensis of CHC,
the following possibilities have been proposed: 1st, the CC component arises from the main HCC tumor, and 2nd,
the entire cancer arises from a stem cell potentially differentiating into hepatocytes and bile duct epithelium.
In this review, I will describe the tumorigenesis of CHC and introduce the hepatic stem cell, such as hepatic
progenitor cells.
- Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
-
Jung Hyun Kwon, Si Hyun Bae, Jung Pil Suh, Ho Sung Park, Chan Ran You, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Dong Hoon Lee, Ho Jong Chun, Byung Gil Choi, Chan Kwon Chung, Eun Sun Jung, Mi Ryung Ryu
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):49-54. Published online June 30, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 43 year-old-women patient was admitted for one month of jaundice. She was diagnosed hepatitis B carrier
17 years ago and has not done a routine check. Abdominal CT showed a large ill defined mass in left hepatic lobe
with inhomogenous enhancement in arterial and delayed phase. The result of biopsy including the
immunohistochemical stains showed the combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma (stage IVa, type C by
Allen and Lisa). With the radiation therapy (3,910 cGy), six times of transarterial chemo-lipiodolization and two
times of percutaneous ethanol injection, huge mass was markedly decreased in size and no stain in hepatic
angiogram. She underwent left lobectomy.
- A Case of Cyberknife Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis
-
Chan Ran You, Si Hyun Bae, Hyun Young Woo, Soung Won Jeong, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Hong Seok Jang, Dong Hoon Lee, Byung Gil Choi
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):82-86. Published online June 30, 2007
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 64 year-old-male patient was transferred to our hospital for infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
without treatment response because of treatment failure and disease progression. He had been diagnosed
infiltrating HCC 9 months ago and then treated with three times of transarterial chemolipiodolization (TACL) in
other hospital. But, HCC was progressed. Abdominal CT showed infiltrating HCC in S7 and a small daughter
nodule in S8 with right and main portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). We performed stereotatic radiosurgery
(Cyberknife) for the treatment of PVTT and four times of TACL for the treatment of intrahepatic HCC every
4weeks. The total radiation doses using with Cyberknife were 36Gy with a prescription isodose 80% in 3 fractions
over the three consecutive days. After treatment, infiltrating HCC was decreased in size and PVTT was markedly
regressed. Response rate of serum AFP was 57.2%. In conclusion, we report the case of good treatment response
in the patient with HCC with PVTT after combination treatment of Cyberknife and TACL.
- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma : Curative Resection after Repeated Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization, Systemic Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
-
So Yeon Lee, Seung Kew Yoon, Min Su Kim, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Byung Gil Choi, Ho Jong Chun, Dong Gu Kim, Seok Whan Moon
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2006;6(1):38-41. Published online June 30, 2006
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 46 year-old male patient was admitted to our hospital for evaluation of hepatic mass which was detected on
ultrasonography. He had a history of chronic hepatitis B carrier. Laboratory findings showed that HBsAg was
positive, and HBeAg was negative. AFP was 2,081.1 ng/mL. Abdomen CT showed a large well-defined low
density lesion involving entire right hepatic lobe which was compatable with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(stage III). Celiac and hepatic arteriogram reveled huge hypervascular mass at both lobe of the liver.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), systemic chemotherapy, percutaneous ethanol injection therapy
(PEIT), and radiotherapy were combined as the treatment of huge hepatoma. After combined therapy, tumor
decreased in size. As a result, curative right lobectomy could be performed. Six months after surgery, chest CT
showed two small metastatic nodules in both lung, so wedge resection was performed. We followed the patient
for 5 years after operation and there was no evidence of regional tumor recurrence or distant metastasis.
- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy
-
So Yeon Lee, Si Hyun Bae, Min Su Kim, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Dong Hoon Lee, Ho Jong Choen
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2006;6(1):52-55. Published online June 30, 2006
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 57 year-old-male patient was admitted to our hospital for evaluation of hepatic mass which was detected on
ultrasonography. He had history of chronic hepatitis B and alcoholism. Laboratory findings showed that HBsAg
was positive, and HBeAg was negative. AFP was 5.39 ng/mL. Abdominal CT showed large ill-defined low
density lesion in 4, 7 and 8 segment of the liver with tumor thrombosis at umbilical portion of left portal vein,
which was compatible with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (stage IVb). Celiac and hepatic arteriogram
revealed huge hypervascular mass at both lobe of the liver. Chemoport catheter was inserted to the right hepatic
artery and intra-arterial chemotherapy (epirubicin 50 mg every 4 weeks, cisplatin 25 mg and 5-FU 200 mg
weekly) was started with continuous infusion device. After 3 cycles of repeated intra-arterial chemotherapy, tumor
mass in both hepatic lobe were decreased in size and extent. He is planned to be treated with additional
intra-arterial chemotherapy.
- Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Dysplastic Nodule
-
Chang Wook Kim, Eun Sun Jung, Jong Young Choi, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon, Chang Don Lee, Kyu Won Chung, Hee Sik Sun
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2004;4(1):50-54. Published online June 30, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Dysplastic nodule (DN) is considered as precancerous lesion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). There are several evidences to support the theory about multistep progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Recently we experienced a patient with HCC of the
odule-in-nodule pattern, namely small HCC within DN, which supported the multistep theory of hepatocarcinogenesis. The tumor was seen as a 3 cm, arterial enhancing mass with delayed wash-out patterns in the segment Ⅶ at helical CT. The patient was treated by surgical resection. A 3.0×2.5 cm mass was seen in the resected specimen. A 2.2×1.5 cm, smaller nodule was observed within this mass, i.e. the
odule-in-nodule pattern. Microscopically, various grades of HCC foci were seen within high grade DN. Because DN does not always progress to HCC, further studies are needed to evaluate what kind of DN has the high possibility of progressing of HCC at last.
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Intrahepatic Duct Invasion Treated with Early Surgical Resection
-
Woo Chul Chung, Young Min Park, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Doo Ho Park, Dong Goo Kim
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2001;1(1):72-76. Published online June 30, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A 40-year old patient with chronic hepatitis B was admitted to our hospital due to right quardrant abdominal pain and jaundice for 2 days. One month ago, he had been treated for acute cholangitis. Total bilirubin was 6.69 mg/dL, AST/ALT level 150/165 IU/L, and AFP 6.7ng/mL. Abdomen CT showed that diffusely irregular tortuous dilatation of IHBD was noted in S 6, more markedly in the peripheral portion, with rather higher density than fluid within lumen, suggesting mucin producing biliary tumor. ERCP demonstrated that a long segment movable filling defect was present at CHD, proximal CBD and posterior right intrahepatic duct. Suggesting sludge and posterior inferior segment of right intrahepatic duct was not visualized with filling defects. At that point we suspected that his diagnosis was cholangiocarcinoma. So we carried out the surgical resection. The pathologic results were hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct invasion. Because of the incomplete resection of hepatocellular carcinoma, TAC was performed twice during the next 2 months. After then he has been taken care at OPD with good condition. This case shows that hepatocellular carcinoma is early detected by bile duct dilatation on CT and successfully treated by surgical intervention and TAC.
|